Quick overview:
Windows-Tweaks bietet schon seit geraumer Zeit einige Tipps zum Beschleunigen des NTFS-Dateisystems an:
Wir zeigen Ihnen nun, wie Sie beide Tipps wesentlich einfacher durchführen können und geben Ihnen einen brandneuen Tipp zum Beschleunigen des NTFS-Dateisystems. Halten Sie sich fest:
Increase the size of the master file table
Lesen Sie hier mehr über die MFT. Um zu verhindern, dass die Master File Table fragmentiert, reserviert das NTFS-Dateisystem permanent 12,5% der Systempartition für die Nutzung der MFT. Geht Ihre Festplattenkapazität zur Neige, werden auch Daten in die MFT geschrieben. Besonders kleinere Dateien mit wenigen Kilobytes werden auch bei genügend Speicher in der MFT gelagert. Dies führt zu einer Fragmentierung, der Sie mit folgenden Schritten vorbeugen können:
1. Klicken Sie auf Start/Ausführen und tragen Sie cmd ein. Bestätigen Sie mit OK.
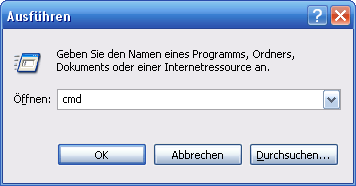 #
#
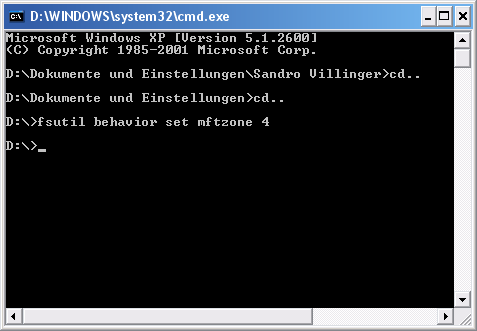
2. Hier können Sie den Befehl „fsutil behavior set mftzone x eingeben, wobei x Werte von 1 bis 4 annehmen kann. Erklärung:
1 = 12.5% of the data carrier
2 = 25% of the data carrier
3 = 37.5% of the data carrier
4 = 50% of the data carrier
The larger the MFT, the lower the chance of fragmentation, although memory consumption can of course also increase.
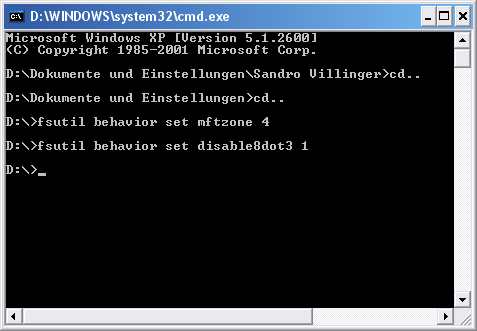
Switch off support for old 8+3 file names
Die Unterstützung für klassische Dateinamen (8+3 Namen wie z.B. alternam.txt aus DOS-Zeiten) verursacht, dass auch bei NTFS sämtliche Dateien intern auch noch als 8+3 Dateinamen vorliegen. Da dies Performance kostet, sollten Sie dies via „fsutil behavior set disable8dot3 1 deaktivieren. Hinweis: Sollten Sie Probleme mit 16-Bit-Applikationen bekommen, deaktivieren Sie dies am Besten via „fsutil behavior set disable8dot3 0 wieder. Lesen Sie auf dieser Seite mehr zu möglichen Problemen!
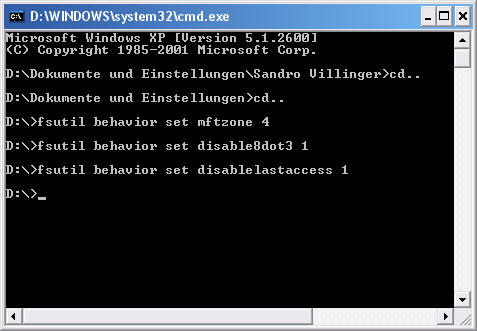
Do not save the last access with NTFS
Und nun zu unserem brandneuen Tipp: Jeder Ordner und jede Datei beinhalten das Attribut „Letzter Zugriff. Dieses zeigt an, wann zuletzt auf die Datei zugriffen oder wann sie verändert wurde. Dieser Zeitpunkt wird zunächst in den Arbeitsspeicher und anschließend an zwei Orte der Festplatte (der Datei selbst und der MFT) geschrieben. Da dies zu erheblichen Leistungsverlusten führen kann, empfehlen wir die Deaktivierung des letzten Zugriffes: Klicken Sie hierzu auf „Start/Ausführen und geben Sie „cmd ein. Tippen Sie nun den Befehl „fsutil behavior set disablelastaccess 1 ein und bestätigen Sie mit Enter!
Wir hoffen, dass wir Ihr System mit diesen NTFS-Tweaks gehörig Beine gemacht haben!
NOTE FOR NEW PUBLICATION: This article was produced by Sandro Villinger and comes from the Windows Tweaks archive, which has been built up since the late 1990s.
On Windows Tweaks you will find time-saving tech guides for PC, software & Microsoft. For a stress-free digital everyday life. Already we have been "tweaking" Windows since 1998 and just won't stop!



