Quick overview:
Die Begriffe "DNS", "Gateway" und "IP" werde Sie wahrscheinlich schon gehört haben - aber was bedeuten sie? Und was haben diese mit einem Router zu tun? Diese und auch andere Fragen versuche ich Ihnen nun zu erklären.
"DNS server" & "IP address":
Alle Computer die an ein Netzwerk angeschlossen sind haben eine Nummer, die sie eindeutig identifiziert. Es wird unterschieden zwischen privaten und öffentlichen IP-Adressen. Jeder Computer, der sich in das Internet einwählt bekommt eine öffentliche Adresse wie z.B. 217.230.23.3. Eine private IP-Nummer ist für Netzwerke gedacht, die nicht direkt im Internet sind, wie z.B. kleine Heimnetzwerke und ähnliches. Für ein privates Netzwerk bietet sich folgender Adressbereich an: 192.168.0.X - 192.168.0.X. Jeder Computer in eurem Heimnetzwerk sollte eine IP in diesem Adressbereich besitzen. Die IP 192.168.0.1 ist in den meisten Fällen schon von dem Router belegt!
Jetzt bleibt noch die Frage nach dem DNS-Server offen. Wir wissen jetzt, dass jeder Computer im Internet über seine IP Adresse angesprochen wird. Aber warum müssen Sie dann nicht in Ihren Browser http://212.227.127.81/ eingeben um www.windows-tweaks.info zu erreichen ?
Hier kommen der DNS-Server ins Spiel. Die Aufgabe eines DNS Servers besteht darin, Ihnen das Leben leichter zu machen. Es lässt sich ja viel leichter z.B. windows-tweaks.info merken, als die IP-Addresse des Servers auf dem die Windows-Tweaks Homepage liegt. Wenn Sie in Ihren Browser www.windows-tweaks.info eingeben, dann wird eine Anfrage an einen DNS Server gestellt, der Ihrem Browser die IP des Servers, auf dem die Homepage liegt, zurück- gibt.
Wenn Sie selbst herausfinden wollen, welche Homepage auf welchem Server liegt, oder einfach nur testen wollen, ob Sie eine Verbindung zu einem DNS Server haben, dann können Sie das folgendermaßen überprüfen:
Klicken Sie auf Start/Ausführen und geben Sie cmd (unter Windows 98/Me: command) ein. Tippen Sie nun ping www.windows-tweaks.info ein!
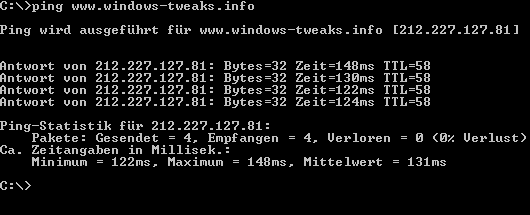
Sie sehen eine IP-Adresse in der Klammer hinter der Homepage. Hier im Beispiel ist die Adresse von windows-tweaks.info 212.227.127.81. Wenn Sie aber jetzt http://212.227.127.81 ausprobieren, werden Sie feststellen, dass es nicht funktioniert. Dies ist bei sehr vielen Webseiten so: Dies liegt einfach daran, dass die meisten Internetserver nicht den Standartport für Webserver verwenden. Und nun zu dem Thema Gateway:
"Gateway:
Ein Gateway ist, einfach gesagt, ein Computer oder ein Hardware-Router der 2 Netzwerke verbindet. In folgendem Fall wird ein Heimnetzwerk mit dem Internet verbunden. Hier ein Bild um es zu verdeutlichen:
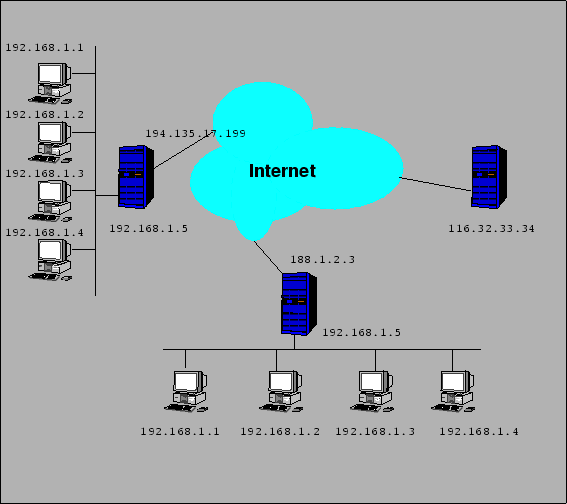
Auf diesem Bild wurde der Adressbereich für die privaten Netzwerke anderst gewählt als bei den obigen Beispielen - ich hoffe, dass dies Sie nicht stört.
Auf diesem Bild sehen wir 3 blaue markierte Rechner. 2 Rechner agieren als Gateway und verbinden ein privates Netzwerk mit dem Internet.
Network settings under Windows 2000/WinXP/Win2003 Server:
So, jetzt kommen Sie zu dem wichtigsten Teil dieses Artikels, den Einstellungen:
1. Die Eigenschaften der Netzwerkumgebung aufrufen:
2. Die Eigenschaften der LAN-Verbindung öffnen:

3. Die Eigenschaften des TCP/IP Protokolls anwählen:
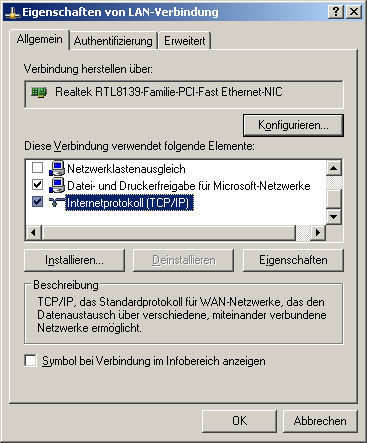
There are now 2 options for setting the DNS server:
Bei der 2. Variante geben Sie den Router als DNS-Server an. Oben haben Sie hingegen gelernt, dass DNS-Server riesigen Speicher haben müssen, um viele Internetadressen zu speichern - den hat aber ein Router nicht. Wenn der Router eine DNS Anfrage bekommt, leitet er sie automatisch an die DNS-Server des Providers weiter. Nicht alle Router unterstützen dies, also ist die 1. Methode die sicherste.
1st possibility:
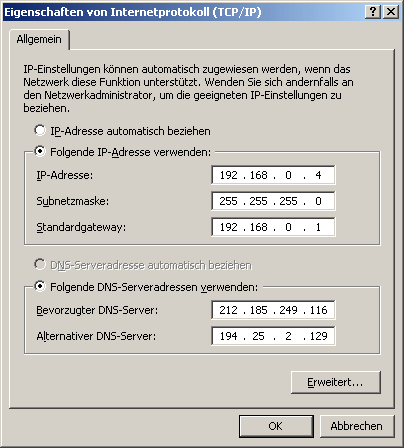
2nd possibility:
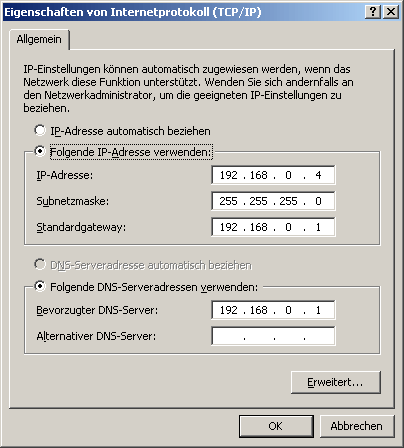
Die eingetragenen DNS-Server auf dem oberen Bild sind sehr zuverlässliche Server von T-Online die jeder benutzen kann.
Router security and common "problems":
Ich will Ihnen nun nicht erzählen, wie alles im einzelnen funktioniert, aber ein paar Grundlagen müssen sein, um die Sicherheit hinter einem Router zu verstehen und die damit verbundenen Probleme lösen zu können. (Beste Beispielt für ein "Problem" : eMule LowID)
Am besten stellen Sie sich das Routing mal so vor: Ihren Computer stellen Sie sich als ein Tor vor und hinter diesem Tor sollen Ihre Anwedungen, wie z.B. eMule und ein WebServer, laufen. Gehen Sie einmal von folgendem Szenario aus: Sie haben ein Netzwerk mit einem Router das so aufgebaut ist, wie das auf dem oberen Bild (unten) der Fall ist. Ihr Router hat die IP 192.168.1.5. Hier nochmal das Bild:

Angenommen, dass der WebServer auf dem Computer mit der IP 192.168.1.4 läuft. Ihr Freund mit der IP 116.32.33.34 versucht jetzt auf den WebServer zuzugreifen. Aber, es geht nicht! Schauen Sie sich die Zeichnung an: Ihr Freund greift auf Ihre öffentliche IP 188.1.2.3 zu. Die Frage ist jetzt: Wo landet er? Die Antwort ist einfach: Auf dem Router - aber da der Router sich von aussen aus Sicherheitsgründen nicht ansprechen lässt, bekommt Ihr Freund eine Fehlermeldung und kann sich nicht verbinden. Die meisten denken, dass eMule ja nur nach aussen connecten muss, aber das stimmt nicht. eMule wartet auf Verbindungen von aussen und kann ohne diese Verbindungen nur eine LowID bekommen. Der Trick ist jetzt, dem Router mitzuteilen, dass er die Verbindungen die an eMule sollen an den Rechner mit eMule weiterleiten soll. Wie das genau geht, kommt immer auf die Anwendung an und wird hier nicht behandelt, da ich nur eine kleine Erklärung geben wollte, was hinter einigen "Problemen" steckt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie hier.
Dieser Gastartikel wurde von Al Capone (aus dem Windows-Tweaks Forum) erstellt, dem ich hier ein ganz großes Dankeschön für seine Mühe aussprechen möchte!
NOTE FOR NEW PUBLICATION: This article was produced by Sandro Villinger and comes from the Windows Tweaks archive, which has been built up since the late 1990s.
On Windows Tweaks you will find time-saving tech guides for PC, software & Microsoft. For a stress-free digital everyday life. Already we have been "tweaking" Windows since 1998 and just won't stop!



